
Did you ever think of the suffering populations by Parkinson’s disease in every part of the world?
This is a generally known and very incapacitating neurodegenerative disease found in millions worldwide. Research shows that in Western Europe, 160 cases of such disease occur with 100,000 populations affected, and up to 4% of over 80-year-old individuals are affected. As the population becomes older, further challenge remain for neurologists and primary care physicians in the diagnosis and management of the condition.
In this blog, we will go through the complexities of this disease along with its recent research and the future possibilities of persons affected by it.
Just like tau in Alzheimer’s disease, alpha synuclein is a misfolded protein in Parkinson’s disease.
Here’s what happens.
Stress-Related Misfolding: A lot of oxidative stress in brain causes misfolded alpha-synuclein (NINDS, 2015).
Formation of Lewy Bodies: These misfolded proteins form aggregates called Lewy bodies.
Damage to Dopamine Neurons: Lewy bodies accumulate around these neurons, exerting additional stress. It causes mitochondrial dysfunction and eventually culminates in the death of these essential neurons.
This chain of events lends itself to the progression and symptomatology of the disease.
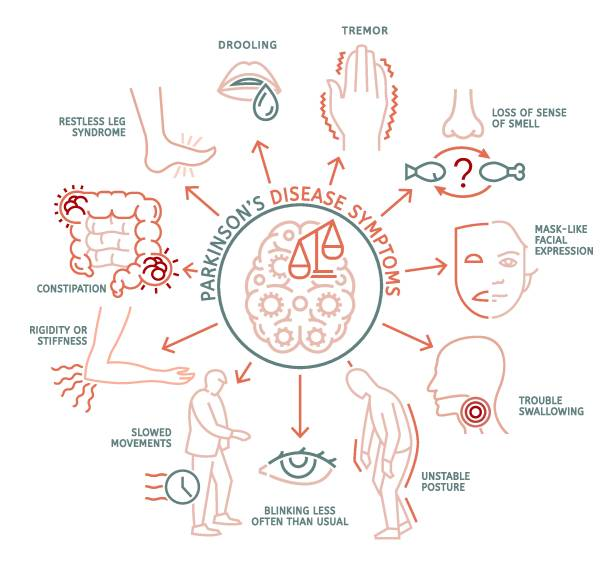
Below are the main symptoms that can differentiate the disease:
Knowing these symptoms can help in early diagnosis and handling of the disease. When you or someone dear to you observes any indicators of the disease, then it is wise to seek out a health provider for the necessary review and care.
This disease happens due to a mix of factors that can raise susceptibility to the condition. Such causes and risk factors have to be understood because some are manageable, and others cannot be changed.
Age increases the risk of getting Parkinson’s as from the age of 60; this risk becomes steeper. Genetic inheritance comprises specific mutations which increase the risk of this condition. Men indeed tend to have a greater susceptibility to diseases than women.
Mitochondrial defects are the major cause of Parkinson’s disease (Jankovic & Tan, 2020). Mitochondria are the organelles that serve as an energy source for the body’s cells. If there is malfunctioning, it leads to neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, damage to brain cells in the body caused by inflammation and oxidative stress is the ultimate cause of Parkinson’s disease.
Repeated head trauma, as with contact sports athletes, increases susceptibility to developing Parkinson’s disease later in life. Trauma to the brain fastens brain cell damage and results in the condition.
There is a wide range of other chemicals, such as pesticides and herbicides are found in agriculture use. All of them pose a heightening risk of developing the disease Parkinson’s disease. Exposure to these deadly chemicals leads to harm and disruption in the brain cells.
Long-term exposure to such heavy metals leads to higher risk of the disease. Such metals may accumulate in the body, damage the brain over time, and possibly cause Parkinson’s disease.
Calcium plays an active role in the functionality of the brain. Disruption in calcium metabolism could lead to wrong signaling in terms of calcium metabolism by the brain cells. It leads to Parkinson’s at the disorders at the first stage.
Mental health is a vital constituent of well-being. Chronic stress or depression creates the base that predisposes a person to significant risks of developing Parkinson’s disease. Stress really has an adverse impact on brain cells, leading to neurodegenerative diseases.
The evident recreational drugs, amphetamines can cause brain damage which eventually leads to Parkinson’s disease. These substances alter the brain chemistry to a pattern that may lead to showing Parkinson’s symptoms later in life.
Basically, Parkinsonism diagnosis is by way of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. So, advanced imaging modalities are used to confirm diagnosis and rule out similar diseases.
It is diagnosed primarily based on the history and physical examination of the patient along with his symptoms and signs.
This is a scan that marks the difference between essential tremor and Parkinson’s disease.
It is done to look for some abnormalities in the affected areas of the brain. This ensures a clear diagnosis that ultimately turns toward a successful treatment planning where such diagnosis is used together with the doctor’s experience (Peeters).
L-Dopa is one of the highly researched and known drugs that help in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. It increases the levels of mediator dopamine in the brain.
Here are the ways of how it works and the important things to know about it:
Even though they belong to the same family, dopamine can’t pass the central nervous system but L-Dopa does. When L-Dopa penetrates it gets converted into dopamine to manage the symptoms of disease.
The identical amino acid decarboxylase enzyme is also used by neurons that produce serotonin to convert L-Dopa to dopamine.
L-Dopa, can harm serotonin neurons that can lead to negative psychological effects.
Often, L-Dopa drugs come with an adjunct, the decarboxylase inhibitor. It prevents L-Dopa from being changed into dopamine outside the brain, thereby allowing more dopamine to reach the site of its action.
Vitamin B6 might interact with decarboxylase inhibitors. So, it is advised not to pair it up with L-Dopa medications.
L-Dopa is derived from amino acid tyrosine. So, having protein-rich food consumed following medication will aid in its passage into the brain.
Thus, comprehension of the practical mechanism of L-Dopa must be well learned by those who want to use it to manage symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and better their living quality.
Parkinson’s disease indeed seems really difficult and challenging. However, with the current establishment of research and treatments, it has a future.
There is progress made by understanding how proteins like alpha-synuclein work, much better medications such as L-Dopa, and discovering new treatments. Early diagnosis good treatment and better lifestyle can help a lot. It is important to stay hopeful and to support each other as we always learn something new in order to tame the effects of the disease with what is found. One day, we can imagine a future where Parkinson’s does not hinder anyone.
So what do you think? In the future, can we possibly bring such treatments that would be better than this or may be a cure?
Parkinson’s Disease: challenges, progress, and promise. (2015). National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). https://www.ninds.nih.gov/current-research/focus-disorders/parkinsons-disease-research/parkinsons-disease-challenges-progress-and-promise
Jankovic, J., & Tan, E. K. (2020). Parkinson’s disease: etiopathogenesis and treatment. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 91(8), 795–808. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-322338
Peeters, E. Shaking Free: A Journey with Parkinson’s.